Using variables in Plans
Variables are used throughout plans to pass information from one node to another, or to store the result of a dynamic computation.
Variable types
Similar to any programming language, Step supports the use of variables in Plans. The variables declared and used in a Plan are called Plan variables. A Plan variable is a container that stores a data value under a specific name.
Like in classical programming languages, Step supports the following types of variables:
- String: stores text (Default type of variables in Step)
- Number: can be integer, long, float, or double
- Boolean: stores values with two states: true or false
- Complex Java objects: lets you define expressions for performing advanced data handling
When passing or setting a variable into the value field of a control or Keyword input, Groovy execution will be required for numbers, booleans, and complex Java objects. The Groovy toggle is a powerful feature in Step that lets you add dynamic behavior to a plan without modifying your Keywords.
Declaring variables in Plan
In Step, you have different ways to declare Plan variables:
- Using Set control: the most common way to declare a Plan Variable is to use the dedicated Set control in your Plan
- Using Parameters: Parameters declared in the web interface under Parameters are made available to the Plan as Variables
- Using Execution Parameters: Execution Parameters selected at the start of execution (Environment, etc) are also made available to the Plan as Variable. See Executing a Plan
Variables in Set control
Using the Visual Plan editor, you can use the Set control as follow to declare a variable:
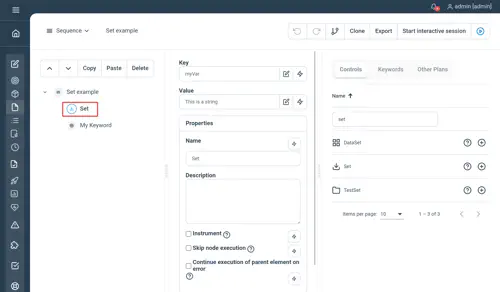
This would declare a variable called “myVar” as String and set its value to “This is a string value”.
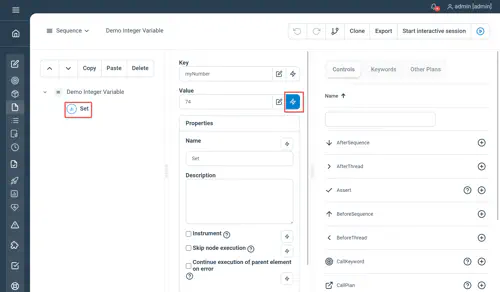
To declare a variable as an integer, toggle the dynamic field button as follow:
Using the plain text editor, you can use the Set control as follows to declare a variable:
Set city="Basel"
MyKeyword Parameter1="Welcome to ${city}"
Set City="Bern"
MyKeyword Parameter1="Welcome to ${city}"Similar to the Visual Plan Editor, you can also use Groovy expressions in the declaration of variables .
Set birthyear=2006
Set age=2019-birthdayIn this case, the variable “birthyear” will be declared as integer. The variable “age” will also be declared a integer as the result of the operation “2019-birthday”
Find out about all possibilities in our Javadocs
See also Controls
Variables in Parameters
Parameters declared in the web interface through the Parameters page are automatically declared by Step as variables at the beginning of the execution and can thus be accessed in the Plan like any other Plan variable.
Variables in Execution parameters
The parameters selected for the execution of a Plan (like “Environment”) are called Execution parameters. These Execution Parameters are also declared by Step as Plan variables at the beginning of the execution and can be accessed in the Plan like any other Plan variable.
Accessing variables
Variables can be accessed practically everywhere in Plans and can also be passed to Keywords.
Using the Visual Plan Editor, you can access previously defined variables in every field that has the dynamic field button as shown in the following screenshot. The variables are available as binding in Groovy expressions.
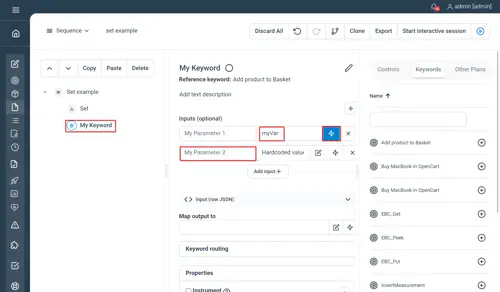
In this example, we pass the content of the variable “myVar” to the first parameter of the Keyword “My Keyword”.
Using the plain text syntax you can use the following syntax to access the content of previously declared variables:
Set birthyear=2013
Set age=2019-birthyear
Set city="Lucerne"
MyKeyword Parameter1="I was born in ${city} in ${birthyear} and I am now ${age} years old"This would call the Keyword “MyKeyword” and set the value of variable “Parameter1” to “I was born in Lucerne in 2013 and I am now 6 years old”
Find out about all possibilities in our Javadocs