Controls
Step controls help to design and structure test plans. They offer various functionality such as variable assignment, control structure or data source definition.
General controls
Set
Sets a value to a variable, which can then be accessed throughout Plans and sub Plans. Combined with the power of groovy, almost anything can be achieved in a Set node.
Properties
- Key : the name of the variable where Step will write to
- Expression : a string or a groovy expression to be interpreted (with groovy evaluation enabled)
Examples
Properties
There is no specific property using this control with natural language, see below example for usage.
Examples
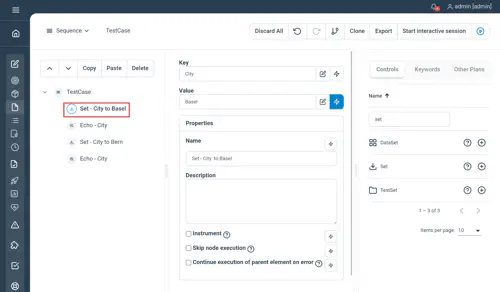
// Set - City to Basel
Set City="Basel"
// Echo - City
Echo City
// Set - City to Bern
Set City="Bern"
// Echo - City
Echo CityNot yet documented.
Echo
Used to print data in the report nodes of a plan, mostly for debugging or information purposes
Properties
- Text : the data you want to display (can be a groovy expression if Groovy mode is toggled)
Examples
Properties
There is no special property in natural language.
Examples
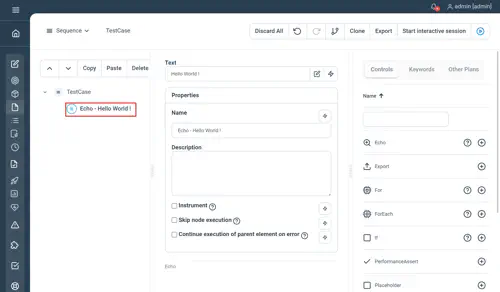
// Echo - Hello World !
Echo "Hello World"Not yet documented.
Sleep
Causes the thread to sleep
Properties
- Duration : the amount of time to sleep.
- Unit : ‘ms’ for milliseconds (default), ’s’ for seconds and ’m’ for minutes.
- Advanced :
- Release Tokens : release tokens reserved in current session (details).
Examples
Properties
- Duration : the amount of time to sleep.
- Unit : ‘ms’ for milliseconds, ’s’ for seconds and ’m’ for minutes.
- ReleaseTokens: (optional, default is false) release tokens reserved in current session (details)
Examples
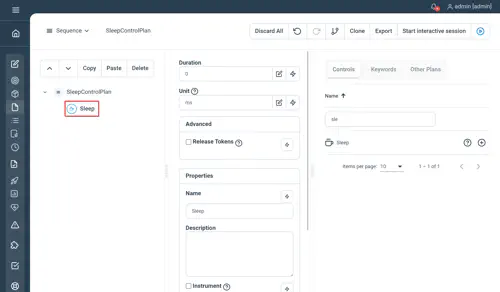
// Sleep control with a duration of 3 seconds
Sleep Duration=3 Unit="s"
//Optional parameter 'ReleaseTokens' (false by default)
Sleep Duration=100 Unit="ms" ReleaseTokens=true
// Simplified syntax (ReleaseTokens option and Groovy String interpolation not supported)
Sleep 100ms
Sleep 1m
Sleep 1hNot yet documented.
Script
Executes any arbitrary groovy code. The script context is local, which means that variable used in the script control cannot be accessed externally by other nodes.
Properties
- Script: the groovy code to be executed
Examples
Properties
There is no special property in natural language.
Examples
-
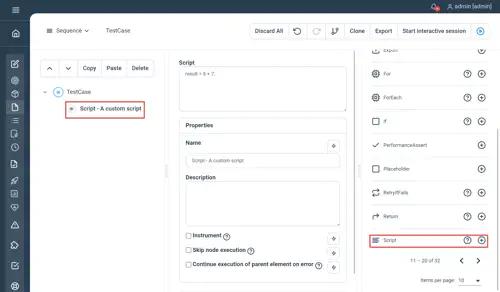
// Script - A custom script
Script
result = 5 + 7;
-Not yet documented.
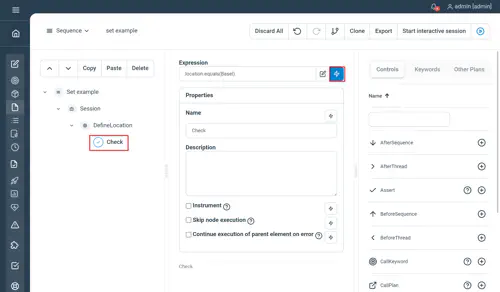
Check
Asserts the given expression, useful for validating the output of the parent node.
Properties
- Expression : the expression to be asserted
Examples
Properties
- Expression : the expression to be asserted
Examples
// DefineLocation
DefineLocation
// Check the return value
Check Expression=previous.location.toString().equals('Basel')Not yet documented.
Assert
Validates the output of a keyword execution.
Properties
- Output attribute : the key containing the data needed for verification
- Operator : the type of verification.
- Expected value : the value you want to check against
- Negate the assertion: tick the box to enable the negation of the value you want to check against
- Custom error message: display a custom error message when the assertion fails
Available operator values are :
- equals : asserts true if the specified output attribute value and the expected value are strictly equals
- begins with : asserts true if the specified output attribute value begins with the expected value
- contains : asserts true if the specified output attribute contains the expected value
- ends with : asserts true if the specified output attribute value ends with the expected value
- matches : asserts true if the specified output attribute value matches the expected value (regular expression can be used as expected value)
- less than (less than or equals): asserts true if the specified numeric output attribute value is less than (or equal to) the expected value
- greater then (greater than or equals): asserts true if the specified numeric output attribute value is greater than (or equal to) the expected value
- is null: asserts true if the specified output attribute value is null or the output attribute is missing
Examples
Properties
There is no specific property using this control with natural language, see below example for usage.
Examples
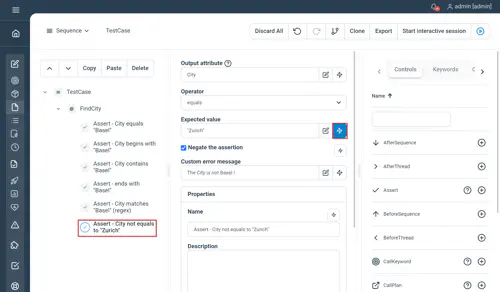
// FindCity
FindCity
// Assert - City equals "Basel"
Assert City = "Basel"
// Assert - City begins with "Basel"
Assert City beginsWith "Basel"
// Assert - City contains "Basel"
Assert City contains "Basel"
// Assert - City ends with "Basel"
Assert City endsWith "Basel"
// Assert - City matches "Basel" (regex)
Assert City ~ "Basel"
// Assert - Count is less than 10
Assert Count < 10
// Assert - Count is less than or equal to 10
Assert Count <= 10
// Assert - Count is greater than 10
Assert Count > 10
// Assert - Count is greater than or equal to 10
Assert Count >= 10
// Assert - City is missing or null
Assert City isNullNot yet documented.
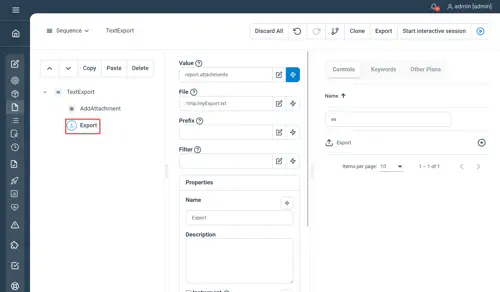
Export
Give the possibility to export the execution attachments to a specific location on the Step Controller.
Properties
- Values : has to be “report.attachments” with groovy evaluation enabled
- File : the file or directory path where to export the attachments
- Prefix : prefix to be prepended to the exported file names
- Filter : regular expression to use in order to filter files to export on their name
Examples
This control is not supported using natural language.
Not yet documented.
Control Structure
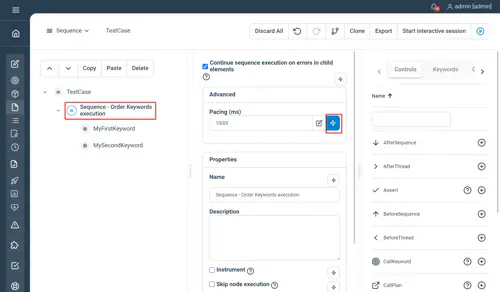
Sequence
Guarantees the ordering of the child nodes, as displayed in the tree. Idea is to group nodes defined to be executed together.
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
Properties
- ContinueOnError : <true|false> specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
// Sequence - Order Keywords execution
Sequence ContinueOnError = true Pacing = 1000l
// MyFirstKeyword
MyFirstKeyword
// MySecondKeyword
MySecondKeyword
EndNot yet documented.
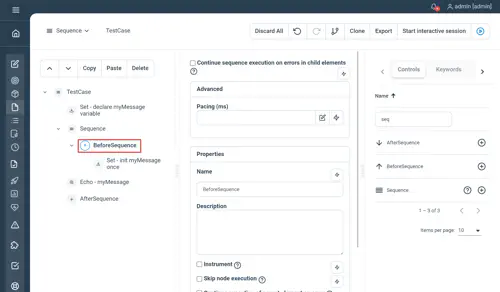
BeforeSequence
Used to perform initialization inside a Sequence, i.e the content within the BeforeSequence control will be executed only once before the Sequence starts. Useful in combination with a For / While loop which have an implicit sequence for each iteration.
In case of multi-threaded executions you also have the possibility to execute an init sequence once and only once before each thread starts (see beforethread).
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
//Set - declare myMessage variable
Set myMessage=''
Sequence
BeforeSequence
//Set - init myMessage once
Set myMessage="Hello World"
End
//Echo - myMessage
Echo myMessage
EndNot yet documented.
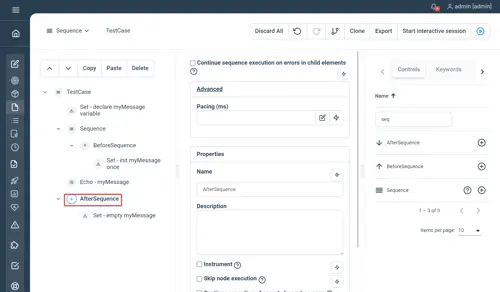
In case of multi-threaded executions you also have the possibility to execute an after sequence once and only once after each thread terminates (see afterthread).
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
//Set - declare myMessage variable
Set myMessage=''
Sequence
BeforeSequence
//Set - init myMessage once
Set myMessage="Hello World"
End
//Echo - myMessage
Echo myMessage
//AfterSequence - cleanup myMessage variable
AfterSequence
//Set - empty myMessage
Set myMessage=""
End
EndNot yet documented.
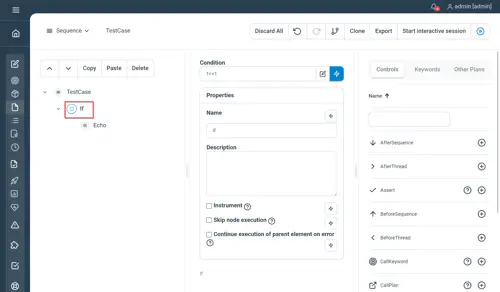
If
Only executes the child nodes if the condition is met.
Properties
- Condition : the expression evaluated to know if the content of the node is executed
Examples
Properties
No condition for this control used with natural language. See below example for usage.
Examples
If 1==1
Echo "Condition met"
EndNot yet documented.
Switch / Case
Same as in any programming language, this 2 controls work in combination.
Switch property
- Expression : the expression to switch on to
Case property
- Value : the value to be potentially matched
Examples
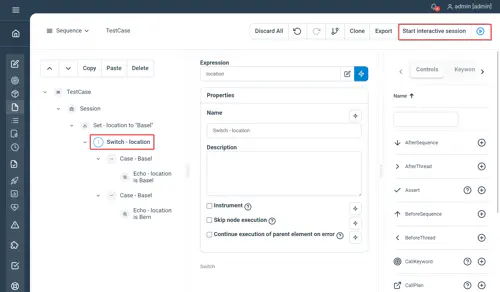
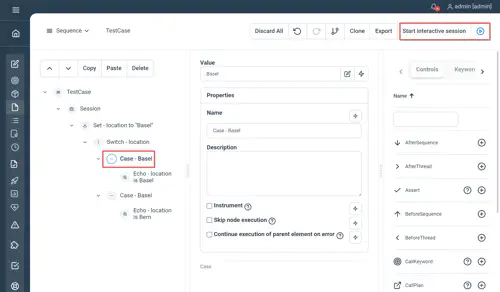
This controls are not supported using natural language.
Not yet documented.
Synchronized
Guarantee thread safety within a test block by synchronizing all threads on the entire Test Execution. Additionally, by using the lock name and the global lock properties, you can synchronize threads across different blocks and test executions.
Properties
- Lock name: the name of the lock, leave empty if you want this lock to synchronize on this plan node
- Global lock: select this check-box if you want this lock to be global across all the executions
Examples
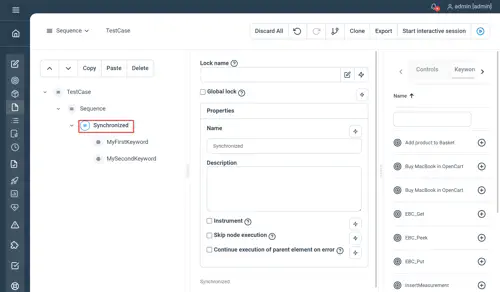
Properties
- LockName: (optional) when unspecified, synchronization happens on this plan node
- GlobalLock: (optional) set this property to true if you want this lock to be global across all the executions
Examples
Synchronized LockName="myLockName" GlobalLock=true
// MyFirstKeyword
MyFirstKeyword
// MySecondKeyword
MySecondKeyword
EndNot yet documented.
For
Creates a For loop at execution time and iterates through its children
Properties
- Start : the initial value of the for loop
- End : the final value of the for loop (exit condition)
- Increment : the increment value at the end of each iteration
- Counter variable (handle) : the name of the variable containing the value of the iteration counter
- Number of threads : the number of threads to use in order to parallelize the loop (i.e the execution of the children)
- Maximum number of failures : the number of failures before the loop is stopped. If empty, the loop is never stopped
Examples
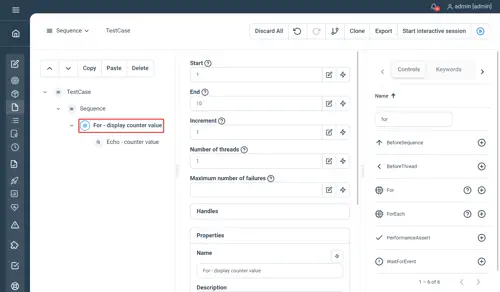
Properties
- Start : the initial value of the for loop
- End : the final value of the for loop (exit condition)
Examples
// For - display counter value
For 1 to 10
// Echo - counter value
Echo counter
EndNot yet documented.
While
Iterates over the node content until the condition is not met
Properties
- Condition : a groovy condition to be evaluated at the beginning of each iteration
- Post Condition : a groovy condition to be evaluated at the end of each iteration
- Pacing: : minimum execution time in ms for the node content to be executed as an Long
- Timeout : stop the control execution after the defined value as a Long (serves as a security)
- MaxIterations : stop th control execution after the define amount of iterations (serves as a security)
Examples
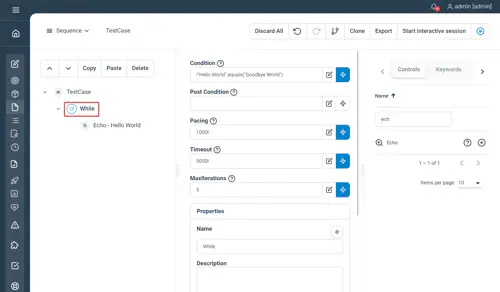
Properties
- Condition : a groovy condition to be evaluated at the beginning of each iteration. Please mind the “|” surrounding the condition expression.
- Post Condition : a groovy condition to be evaluated at the end of each iteration. Please mind the “|” surrounding the condition expression.
- Pacing: : minimum execution time in ms for the node content to be executed as an Long
- Timeout : stop the control execution after the defined value as a Long (serves as a security)
- MaxIterations : stop the control execution after the define amount of iterations (serves as a security)
Examples
-
// While
While
Condition=|!"Hello World !".equals("Goodbye World !")|
Pacing=1000l
Timeout=5000l
MaxIterations=5
-
// Echo - Hello World
Echo "Hello World"
EndNot yet documented.
Keyword calls
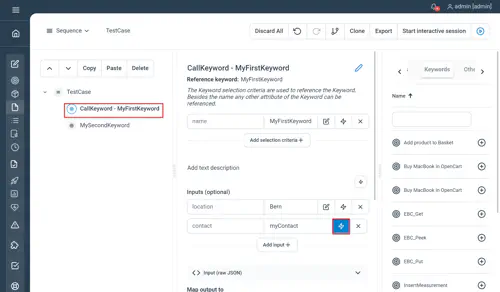
CallKeyword
Technical node used as part of keyword invocation. Can be used explicitly in order to template keyword calling, due to exposure of the “name” input.
Properties
Same as in a regular Keyword call, but a name should be set in order to tell Step which Keyword needs to be called. Used in conjunction with groovy, this can provide a powerful mechanism for Keyword Call templating.
Examples
Properties
Same as in a regular Keyword call, but a name should be set in order to tell Step which Keyword needs to be called. Used in conjunction with groovy, this can provide a powerful mechanism for Keyword Call templating.
Limitations
You can only have String variable using natural language (i.e boolean, numbers and date are not supported). You can however use the Groovy String interpolation to resolve variable value directly in a String. Application prefixed keywords syntax is supported as well as Application / Keyword having spaces in their name, thus the keyword call needs to be double-quoted when using plain text (see example below).
Examples
// CallKeyword - MyFirstKeyword
MyFirstKeyword location="Bern" date="01.07.2019" contact="${John Doe}"
// My Application -> My Second Keyword
"My Application.My Second Keyword"Not yet documented.
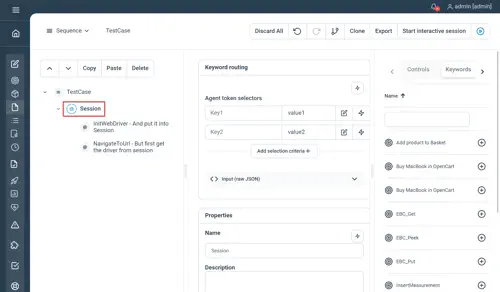
Session
Guarantees that the same session will be used for every child node’s execution (very important for stateful keywords which rely on a certain state as an initial condition). The session control also provide to Keywords the ability to share objects.
You may use keywords which will be executed on different token’s type (i.e. java, .net,…) in the same session control. This implies that one token per type will be reserved. Also, consider that sharing objects between keywords of different type is not supported.
Properties
- Keyword routing : optional, for affinity patterns using selection criteria
Examples
Properties
- Keyword routing : optional, for affinity patterns using selection criteria (see below example for usage)
Examples
// Session
Session key1=value1 key2=value2
// InitWebDriver - And put it into session
InitWebDriver
// NavigateToUrl - But first get the driver from session
NavigateToUrl
EndNot yet documented.
Plan calls
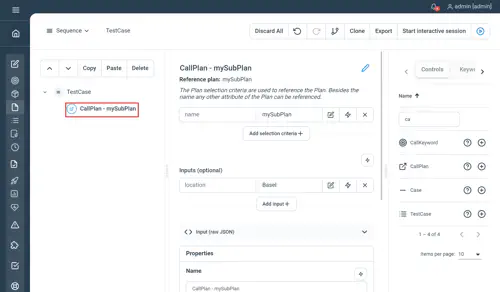
CallPlan
Used to invoke a plan from within another plan
Properties
- keys & values : the plan you want to invoke, as for Keywords and CallKeywords, CallPlan can be used for templating Plan executions.
Examples
Properties
The only property exposed at the moment is the plan name to be called, passing inputs is not supported in natural language yet.
Examples
-
// Call Plan - mySubPlan
Call plan "mySubPlan"
-Not yet documented.
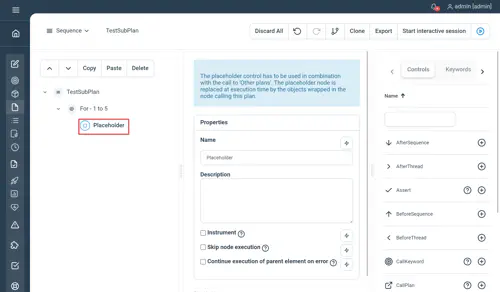
PlaceHolder
Used to execute plan chunks passed from another plan. In conjunction with a plan call, this will be used to defer and delegate the execution of children nodes to another plan. The placeholder needs to be placed inside the target sub-plan as a positional marker. The delegated nodes should be set as children of the sub-plan’s node within the parent plan.
Properties
There is no specific property configurable for this control.
Examples
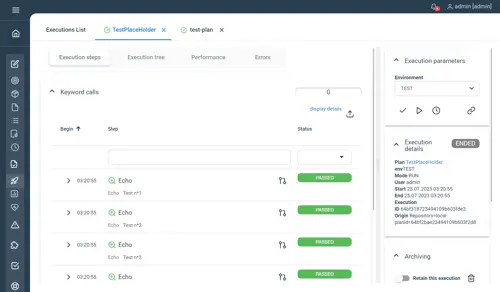
Main plan echoing the counter value while the for loop incrementing the counter is defined in a sub-plan as a placeholder :
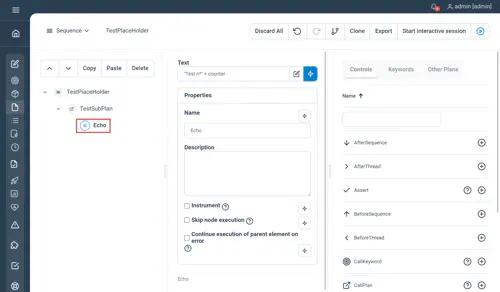
Execution results :
This control is not supported using natural language.
Not yet documented.
Functional Testing
TestCase
Specific container for a group of nodes, will activate the top-level panel in the execution view for high-level test case execution monitoring.
Properties
Simply wrap your Test Plans with a test case
Examples
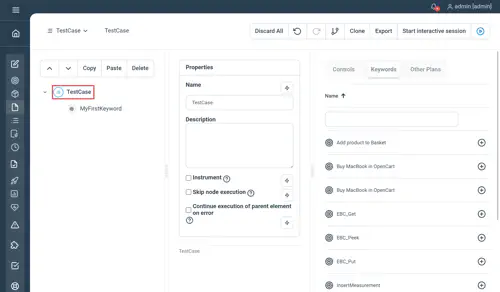
Properties
Simply wrap your Test Plans with a test case
Examples
TestCase
// MyFirstKeyword
MyFirstKeyword location="Bern" date="01.07.2019" contact="${John Doe}"
EndNot yet documented.
TestSet
Used to group up TestCase’s as a single unit and executing them in parallel
Properties
Simply wrap your TestCase’s with a TestSet controller, parallelism is derived from the global variable tec.execution.threads
Examples
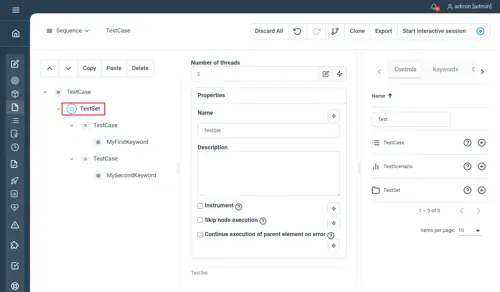
Properties
Simply wrap your TestCase’s with a TestSet controller, parallelism is derived from the global variable tec.execution.threads
Examples
TestSet
TestCase
// CallKeyword - MyFirstKeyword
MyFirstKeyword location="Bern" date="01.07.2019" contact="${John Doe}"
End
TestCase
// CallKeyword - MySecondKeyword
MySecondKeyword
End
EndNot yet documented.
Load testing
ThreadGroup
Starts multiple threads which will execute the node content in parallel
Wizard
With the wizard the values for number of threads and iterations per thread can be easily calculated. It requires the following information:
- Target throughput : the expected number of iterations produced over specified time during the execution
- Estimated iteration durations max : the duration to execute one iteration under load, considering to keep sufficient margin. If the actual iteration time is higher during the execution, the target throughput will not be reached.
Properties (Advanced)
- Number of threads : the number of threads to be started in parallel
- Number of iterations per thread : how many times the node content should be executed per thread
- Pacing : defines a fixed time window in milliseconds, as an Integer, in order to better control the number of keywords executed per time unit (and so that throughput remains independent from keyword execution time)
- Rampup : the ramp-up value is designed to be automatically divided by the number of threads to start them progressively and “spread” them out evenly, it represents the total duration of the ramp-up phase. If the ramp up value is left empty, then it will default to the pacing value (all threads will be spread out evenly but started “quickly”, i.e in one single pacing period).
- Start offset : the duration in ms to wait before the Rampup starts as an Integer
- Maximum duration : the maximal execution time in ms for the whole thread group as an Integer
Examples
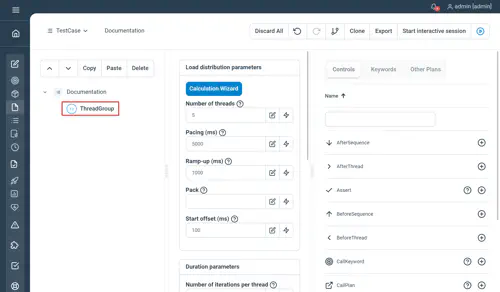
Properties
- Threads : the number of threads to be started in parallel
- Iterations : how many times the node content should be executed per thread
- Pacing : defines a fixed time window in milliseconds, as an Integer, in order to better control the number of keywords executed per time unit (and so that throughput remains independent from keyword execution time)
- Rampup : the ramp-up value is designed to be automatically divided by the number of threads to start them progressively and “spread” them out evenly, it represents the total duration of the ramp-up phase. If the ramp up value is left empty, then it will default to the pacing value (all threads will be spread out evenly but started “quickly”, i.e in one single pacing period).
- Offset : the duration in ms to wait before the Rampup starts as an Integer
- MaxDuration : the maximal execution time in ms for the whole thread group as an Integer
Examples
-
// ThreadGroup
ThreadGroup
Threads=5
Iterations=5
Pacing=5000
Rampup=1000
Offset=100
MaxDuration=25000
-
// Echo - Hello World
Echo "Hello World"
EndNot yet documented.
BeforeThread
Used to perform initialization inside a ThreadGroup, i.e the content withing the BeforeThread control will be executed only once per thread in the ThreadGroup, before the iterations start (so not on every thread iteration).
To define an init section for each and every iteration refer to beforesequence.
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
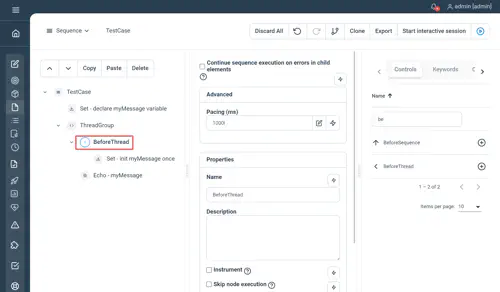
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
//Set - declare myMessage variable
Set myMessage=''
// ThreadGroup
ThreadGroup Threads=2 Iterations=2
BeforeThread
//Set - init myMessage once
Set myMessage="Hello World"
End
//Echo - myMessage
Echo myMessage
EndNot yet documented.
AfterThread
Used to perform clean-up / final tasks inside a ThreadGroup, i.e the content withing the AfterThread control will be executed only once per thread in the ThreadGroup, after the iterations end (so not on every thread iteration).
To define an end section for each and every iteration refer to aftersequence.
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
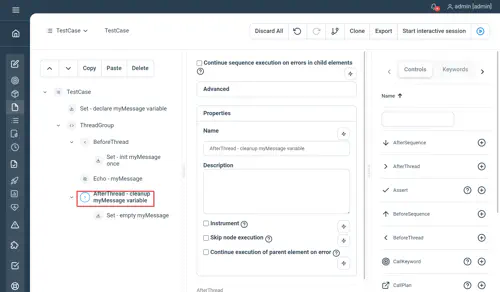
Properties
- Continue sequence execution on error : specify if the sequence should continue until its end if an error occurred within
- Pacing : minimum execution time for the whole sequence to be executed (in milliseconds) as a Long
Examples
//Set - declare myMessage variable
Set myMessage=''
// ThreadGroup
ThreadGroup Threads=2 Iterations=2
BeforeThread
//Set - init myMessage once
Set myMessage="Hello World"
End
//Echo - myMessage
Echo myMessage
//AfterThread - cleanup myMessage variable
AfterThread
//Set - empty myMessage
Set myMessage=""
End
EndNot yet documented.
TestScenario
Usually used to parallelize the execution of multiple ThreadGroups or ‘sub’ plans. Note that all children of a test scenario are executed in parallel independently from their type.
For instance, simply place ThreadGroups as children of the TestScenario to start them in parallel.
Properties
There is no special property for this control.
Examples
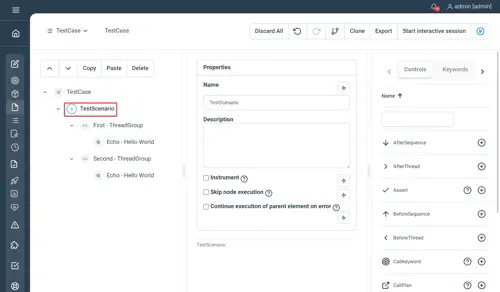
Properties
There is no special property for this control.
Examples
TestScenario
-
// First ThreadGroup
ThreadGroup
-
// Echo - Hello World
Echo "Hello World"
End
-
// Second ThreadGroup
ThreadGroup
-
// Echo - Goodbye World
Echo "Goodbye World"
End
EndNot yet documented.
PerformanceAssert
Validates a measurement metric value (either generated by a Keyword or by a Custom measurement within a Keyword) against a specified value. This control can be placed directly under a Keyword call (to validate a single keyword call generated measurements) or after any kind of loop (to validate a measurement metric aggregation).
Properties
- Metric to assert : the measurement metric to check the value against.
- Measurement name : the measurement name (can be a custom measurement).
- Operator : the operator to use to compare the measurement metric against the specified value
- Value: the value to compare the measurement metric against
Available metrics to assert are :
- average : the average response time of the selected measurement
- min : the minimal response time of the selected measurement
- max : the maximal response time of the selected measurement
- sum : the sum of the response time of the selected measurement
- count : the number of time the selected measurement has been generated
Available operator values are :
- equals : asserts true if the selected measurement metrics value is equals to the defined value
- lower than : asserts true if the selected measurement metrics value is lower than the defined value
- higher than : asserts true if the selected measurement metrics value is higher than the defined value
Unitary example
In the below example, the PerformanceAssert validates that the average response time of the “testKeyword” execution is lower than 3000 ms.
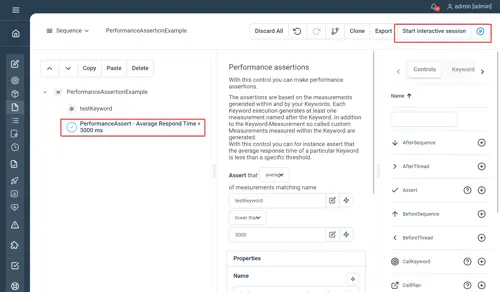
Count example
In the below example, the PerformanceAssert validates that the “testKeyword” has been executed exactly 10 times.
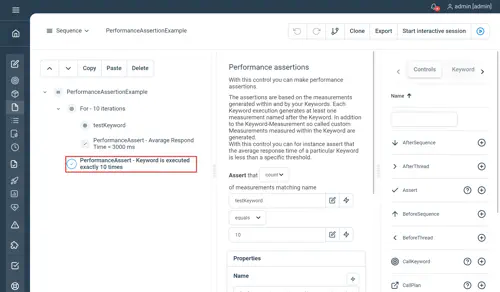
Agreggation example
In the below example, the PerformanceAssert validates that the aggregation done on the average response time of the “testKeyword” over the 10 loop iterations is lower than 3000 ms.

Properties
- Metric (Optional): specifies the metric to be asserted
- Type: String
- Supported values: “Average”, “Max”, “Min”, “Count”, “Sum”
- Default value: If not set the “Average” metric is used per default
- Measurement : specifies the name of the measurement to be asserted. This could be a regex matching several measurements. In this case all measurements will be grouped by name and each group will be asserted individually
- Type: String
- Supported values: any
- Comparator (Optional): the comparator to be used to compare the actual value with the expected value
- Type: String
- Supported values: “equals to”, “higher than”, “lower than”
- Default value: If not set, “lower than” is used per default
- Value : the expected value in ms
- Type: Number
Examples
Example 1:
For 1 to 10
MyFirstKeyword
MySecondKeyword
End
// Assert that the average response time of the Keyword 'MyFirstKeyword' is lower than 100ms
PerformanceAssert Metric = "Average" Measurement = "MyFirstKeyword" Comparator = "lower than" Value = 100Example 2:
For 1 to 10
MyFirstKeyword
MySecondKeyword
End
// Assert that the average response time of the 2 Keywords 'MyFirstKeyword' is lower than 500ms
PerformanceAssert Measurement = ".*" Value = 500Not yet documented.
Synthetic Monitoring
AssertionPlan
An assertion plan declares assertions to be performed on the series of executions of a scheduler task. It is executed after each execution of the scheduler task and triggers an event of type “Assertion of task failed“ upon failure. Typically an assertion plan consists of one or more AssertMetric controls that specify the assertions. AssertMetric can be for instance used to ensure that the number of failures of the executions related to a scheduler task entry remains below a defined threshold.
Note: AssertionPlan must be selected as root of the plan type.
AssertMetric
This control defines a metric-based assertion that can be used within an Assertion Plan to trigger notifications when values of a metric are more or less than a defined threshold for a specific rolling window.
The assert metric control is defined by following properties
- Metric available metrics for the assertion:
- Execution count: count of execution
- Execution failure percentage
- Execution failure count
- Execution failure count by error code
- Response times
- Filters: add custom filters (for instance filter on a specific measurement name Response times metrics)
- Time series aggregation: define which aggregator to use (i.e. average, min, max, sum, percentiles…)
- Time series group by (optional): to aggregate and assert grouping by specified attributes
- Comparator: used for the assertion, can be either below, above or matching threshold
- Threshold value: The values compared to aggregation result using selected comparator
- Error code: defien the code of the error that will be raised if the assertion fails
In below example, we assert that the number of failed executions in the last hour remains below 2:
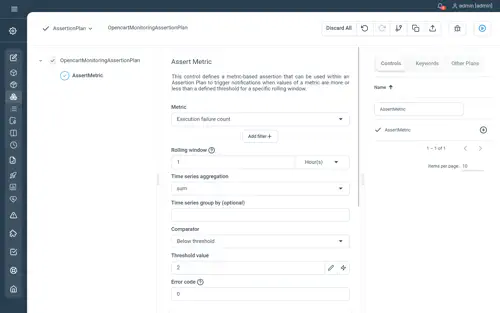
Not yet documented.
Not yet documented.
Data driven controls
DataSet
Used to iterate over rows of data in a table (the table itself can be stored in a database, a file, etc) and can be of different format (json, csv, excel, etc)
Common Properties
- Source type : define the source type object. Values could be : Excel, CSV, SQL, Flat file, Directory, Integer sequence, Json String, Google Sheet V4
- For write : define if the data source will be used to insert values
- Iterator handle : define a variable pointing to the dataset’s iterator
- Rows can then be iterated and accessed with the groovy expression iteratorName.next(), see our example.
- Reset at end : define if once arrived at the end of the data source, the iterator handle should be reinitialized to the first row
Excel properties
- Excel file : the path to your source file
- Worksheet : the worksheet name in your source file (if blank, the first one in your sheet will be selected)
- Headers : check this box if your columns have header
Example

CSV properties
- CSV file : the path to your source file
- Delimiter : the delimiter used in your CSV file
Example
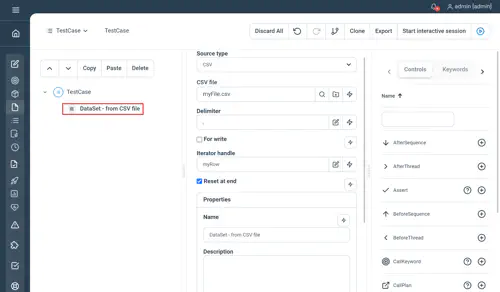
SQL properties
- Connection string : the string used to connect to your database. For example, using jdbc to connect to a MySQL database on localhost : “jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbname”
- Driver class : the driver full class name. For example, using jdbc for MySQL : “com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”
- Query : the SQL query to perform against your database to retrieve the data
- User : the username to connect to your database
- Password : the password to connect to your database. If you want to store your password in a Parameter and thus also protect it, you can use following syntax: “parameter:MyParameterName”. Example: if your password is store in a parameter called “datasource.sql.password”, you can refer to is as follow: “parameter:datasource.sql.password”
- Primary write key : the primary key to use in case you want to write back to your database
Flat file properties
- Flat file : the path to your source file
Directory properties
- Directory : the path to your directory
Integer sequence properties
- Start : value starting the sequence
- End : value ending the sequence
- Inc : increment value for the sequence
Json String properties
- Json string : the JSON document representing your data. The document has to represent of table of values with headers first, and then rows. For example :
{ "pagename" :
["Consulting", "Products"],
"url" :
["https://www.exense.ch/solutions",
"https://www.exense.ch/products"]}Google Sheet V4 properties
- Service Account Key File : the path to your service account key file. Refer to Google documentation about service account key file creation.
- File Id : the Google Cloud unique identifier of your file. It can usually be extracted from the URL locating your file in the Cloud.
- Tab Name : the name of the tab to use in your source file (if blank, the first one in your file will be selected)
Common Properties
- SourceType : define the source type object. Values could be : excel, csv, file (for Flat file) or folder (for Directory). Other source type are not supported yet.
- File : the path to your source file
- ForWrite : define if the data source will be used to insert values
- IteratorHandle : define a variable pointing to the dataset’s iterator
- ResetAtEnd : define if once arrived at the end of the data source, the iterator handle should be reinitialized to the first row
Excel Properties
There is no specific property configurable for Excel sheet in natural language.
Examples
-
// DataSet - from Excel sheet
DataSet
SourceType = "excel"
File = "myFile.xlsx"
IteratorHandle = "myRows"
ForWrite = true
ResetAtEnd = true
-CSV properties
There is no specific property configurable for CSV file in natural language.
Warning: Writing to a CSV file from a dataset is not supported
Examples
-
// DataSet - from CSV file
DataSet
SourceType = "csv"
File = "myFile.csv"
IteratorHandle = "myRows"
ForWrite = true
ResetAtEnd = true
-File properties
There is no special property for “File” type in natural language.
Examples
-
// DataSet - from Flat file
DataSet
SourceType = "file"
File = "myFile.txt"
IteratorHandle = "myRows"
ForWrite = true
ResetAtEnd = true
-Folder properties
There is no special property for “Folder” type in natural language.
Examples
-
// DataSet - from Directory
DataSet
SourceType = "folder"
File = "/myFolder"
IteratorHandle = "myRows"
ForWrite = true
ResetAtEnd = true
- Not yet documented.
ForEach
Creates a ForEach loop based on a collection and iterates through the child nodes.
Common Properties
- Source type : define the source type object. Values could be : Excel, CSV, SQL, Flat file, Directory, Integer sequence, Json String, Google Sheet V4
- Number of threads : the number of threads to use in order to parallelize the loop (i.e the execution of the children)
- Maximum number of failures : the number of failures before the loop is stopped. If empty, the loop is never stopped
- Row handle : define a variable pointing to the current row
Excel properties
- Excel file : the path to your source file
- Worksheet : the worksheet name in your source file (if blank, the first one in your sheet will be selected)
- Headers : check this box if your columns have header
Example
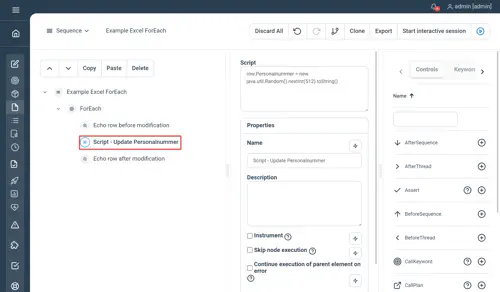
CSV properties
- CSV file : the path to your source file
- Delimiter : the delimiter used in your CSV file
Example
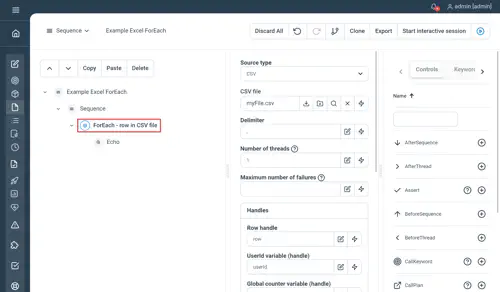
SQL properties
- Connection string : the string used to connect to your database. For example, using jdbc to connect to a MySQL database on localhost : “jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbname”
- Driver class : the driver full class name. For example, using jdbc for MySQL : “com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”
- Query : the SQL query to perform against your database to retrieve the data
- User : the username to connect to your database
- Password : the password to connect to your database
- Primary write key : the primary key to use in case you want to write back to your database
Flat file properties
- Flat file : the path to your source file
Directory properties
- Directory : the path to your directory
Integer sequence properties
- Start : value starting the sequence
- End : value ending the sequence
- Inc : increment value for the sequence
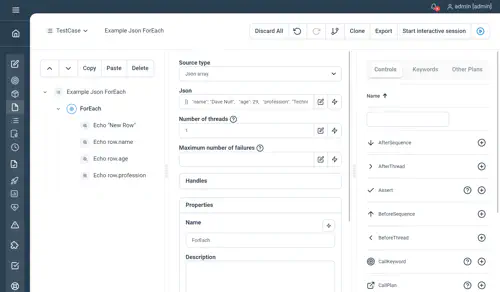
Json array properties
- Json : the JSON document representing your data. The document has to be an array of objects:
[{
"name": "Dave Null",
"age": 29,
"profession": "SysAdmin"
}, {
"name": "Seg Fault",
"age": 54,
"profession": "Developer"
}
]You will then be able to use the Row handle variable as a Json object by, for example, accessing the name and age with row.name and row.age
Example
Google Sheet V4 properties
- Service Account Key File : the path to your service account key file. Refer to Google documentation about service account key file creation.
- File Id : the Google Cloud unique identifier of your file. It can usually be extracted from the URL locating your file in the Cloud.
- Tab Name : the name of the tab to use in your source file (if blank, the first one in your file will be selected)
Json String (Legacy) properties
- Json string : the JSON document representing your data. The document has to represent of table of values with headers first, and then rows. For example :
{ "pagename" :
["Consulting", "Products"],
"url" :
["https://www.exense.ch/solutions",
"https://www.exense.ch/products"]}Common Properties
- SourceType : define the source type object. Values could be : excel, csv, file (for Flat file) or folder (for Directory). Other source type are not supported yet.
- File : the path to your source file
- Threads : the number of threads to use in order to parallelize the loop (i.e the execution of the children)
- RowHandle : define a variable pointing to the current row
- MaxFailedLoop : the number of failures before the loop is stopped. If not set, the loop is never stopped
Excel Properties
- Worksheet : the worksheet name in your source file (if blank, the first one in your sheet will be selected)
Examples
-
// ForEach - row in excel sheet
ForEach
SourceType = "excel"
File = "C:/myFile.xlsx"
Worksheet = "myWorksheet"
Threads = 1
RowHandle = "myRow"
MaxFailedLoop = 2
-
Echo myRow.myColumn
EndCSV properties
- Delimiter : the delimiter used in your CSV file
Examples
-
// ForEach - row in file
ForEach
SourceType = "csv"
File = "/home/myFile.csv"
Delimiter = ";"
Threads = 2
RowHandle = "myRow"
-
Echo myRow.myColumn
End File properties
There is no special property for “File” type in natural language.
Examples
-
// ForEach - row in file
ForEach
SourceType = "file"
File = "C:/myFile.txt"
Threads = 2
RowHandle = "myRow"
-
Echo myRow.myColumn
EndFolder properties
There is no special property for “Folder” type in natural language.
Examples
-
// ForEach - file in folder
ForEach
SourceType = "folder"
File = "/myFolder"
Threads = 2
RowHandle = "myRow"
-
Echo myRow.myColumn
End Not yet documented.
Asynchronous Testing
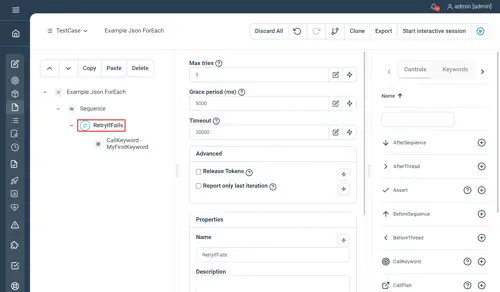
RetryIfFails
Retry mechanism with grace period
Properties
- Max retries : number of retries if child nodes execution fails
- Grace period (ms) : duration to wait in ms after a failed attempt
- Timeout : maximum execution time in ms for the whole execution retries
- Advanced :
- Release Tokens : release tokens reserved in current session (details)
- Report only last iteration: when enabled, only the final iteration will be reported and persisted
Examples
Properties
- MaxRetries : number of retries if child nodes execution fails
- GracePeriod : duration to wait in ms after a failed attempt
- Timeout : maximum execution time in ms for the whole execution retries
- ReleaseTokens: (optional, default is false) release tokens reserved in current session (details)
- ReportLastTryOnly: (optional, default is false) when enabled, only the final iteration will be reported and persisted
Examples
RetryIfFails MaxRetries=3 GracePeriod=5000 Timeout=30000
// CallKeyword - MyFirstKeyword
MyFirstKeyword location="Bern" date="01.07.2019" contact="${John Doe}"
End
//Same example with all properties
RetryIfFails MaxRetries=3 GracePeriod=5000 Timeout=30000 ReportLastTryOnly=true ReleaseTokens=true
// CallKeyword - MyFirstKeyword
MyFirstKeyword location="Bern" date="01.07.2019" contact="${John Doe}"
EndNot yet documented.
WaitForEvent
Wait for a specific event to be receive by the controller. Event can be identified by an eventId or a couple group/name. By default, this control will listen to the local Step controller but a remote one can be specified in its remote properties.
Properties
- Event selection criteria: either select event by id or by group and name (name is optional)
- Event Id: the ID of the event to wait for
- Event Group: the event group to wait for
- Event Name: the event name to wait for
- Polling settings : adapt the polling frequency and control optionally the maximum wait time
- Polling frequency (ms): the interval to poll the event broker in ms as a Long
- Max number of polling: stop waiting for the event after the define amount of iterations (serves as a security)
- Maximum wait time (ms): stop waiting to the event after the defined value as a Long (serves as a security)
- Remote broker settings: to be used when the events are not stored in the local controller
- Remote URL: the Step remote controller URL where to listen to an incoming event
- Remote User: the Step remote controller username to use for connection
- Remote Password: the Step remote controller password to use for connection
- Advanced:
- Release Tokens: release tokens reserved in current session (details)
Examples
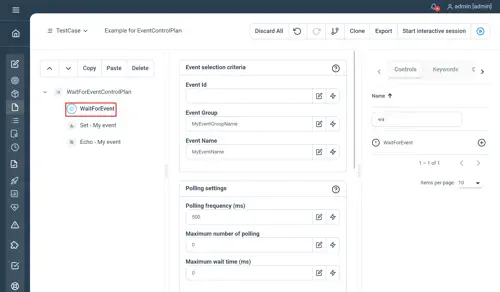
Properties
- EventId: the ID of the event to wait for
- Group: the event group to wait for
- Name : the event name to wait for
- PollingSpeed : the interval to poll the event broker looking for the event in ms as a Long
- Timeout : stop waiting to the event after the defined value as a Long (serves as a security)
- MaxIterations : stop waiting for the event after the define amount of iterations (serves as a security)
- ReleaseTokens: (optional, default is false) release tokens reserved in current session (details)
Examples
-
WaitForEvent
Group="eventGroup"
Name="eventName"
PollingSpeed=1000l
Timeout=5000l
MaxIterations=5
-
// Set - myEvent
Set myEvent=report.getEvent()
// Echo - myEvent
Echo myEventNot yet documented.
Related information
You will find more details on the event broker API and how to effectively use the “WaitForEvent” artefact here.
Composite Keywords
Return
Used within a Composite Keyword, set the Composite output to the returned value(s).
Properties
No property. Just enter key values as you’d like them to be available in the output of a regular keyword.
Examples
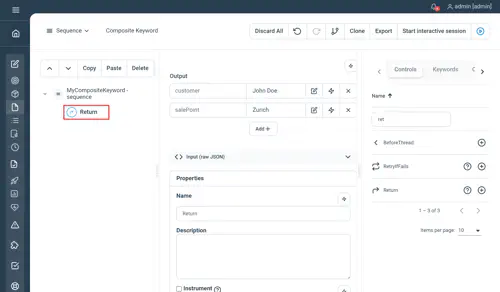
Note
This control is not available as natural language as Composite Keywords cannot be created using natural language yet.
Not yet documented.
Advanced control options
Release Tokens
This advanced option is currently available on controls entering a waiting state, namely:
The option only has an effect when executed inside a session control and must be used with caution. Its main purpose is to release the agent tokens currently reserved by the session when entering an idle state.